
Hi, there!
Need a quick quote or have a pipe support question?

Need a quick quote or have a pipe support question?

Complete this form and an APP representative will be in touch with your quote.
Pipe shoes are a critical type of pipe support that can prevent damage and lengthen the lifespan your process piping systems. This guide describes the role of pipe shoes, the types of shoes on the market today, and how to maximize their efficiency.

Chapter 1
The Need to Strengthen Piping Systems with Pipe Shoes
Your pipes face constant challenges that threaten the life of your process piping system. It’s a set of problems that is built into the very nature of piping, and it plays off a common danger: corrosion.
Piping systems can be deceptive. When they’re running smoothly, it’s hard to see the wear, danger, and deterioration subtly creeping in. However, they’re up against powerful natural hazards.
Pipes carry corrosive materials and often face extreme external climates. Movement and vibrations are inherent, and as heavy metallic structures move, they wear down, corrode, and risk breaking open.
At the same time, changes in temperature stand as another foe to piping systems. Temperature changes can cause heat transfer, promote damaging friction, and create destructive ice formation.
With pipes strained by so many forces, piping systems are up against the constant danger of ruptures and on-site disasters. The good news? Pipe supports can protect pipes from many of the most menacing issues. And as soon as you understand how to fight off the most common destructive forces, you can begin to protect them, too.
Galvanic corrosion is an electrochemical process by which one metal causes another metal to corrode and break down. This type of corrosion requires three things: an anode (one metal), a cathode (a second metal), and an electrolyte (usually water, bacteria, or grime).
Simply put, metals have different physical properties. A more noble metal (the cathode) has a tendency to hold on to its electrons and pull electrons from other sources, whereas more basic metals (the anodes) are eager to give their electrons away. That means that when you connect these dissimilar metal types in an electron-heavy environment, the more basic metal will give its electrons to the more noble metal. When a metal gives up its electrons, galvanic corrosion begins, and the metal will rust.
Pipe supports can protect pipes from many of the most menacing issues.
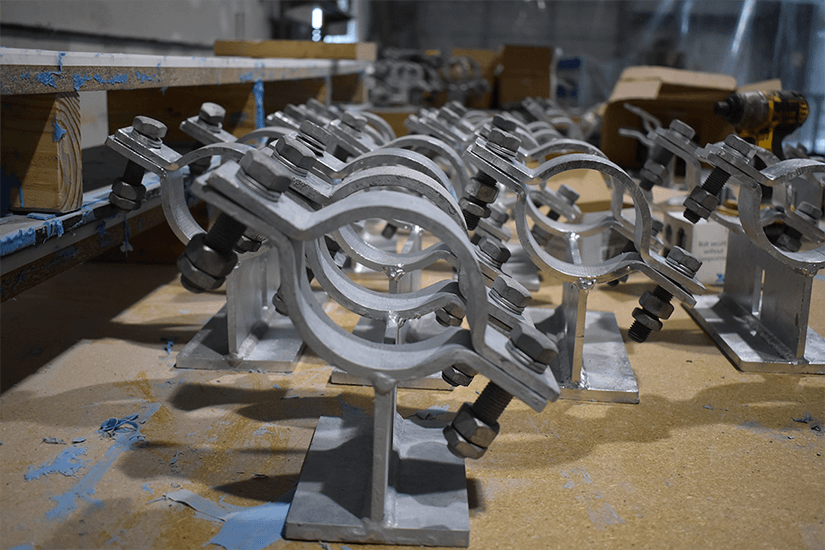
Pipe restraints and fittings can help reinforce systems and stop destruction. However, it’s possible to put too much pressure on these tools, and that can cause more serious problems. Sloppy installation can easily lead to worn parts and broken fittings, which can set off a chain reaction that snaps or collapses other parts within your piping system.
It’s important to get past the common belief that stopping pipe movement altogether is always the best option. Instead, fittings should promote natural, axial movement and reduce friction whenever possible. At the same time, supports need to be able to hold up to vibrations, pressure, and pipe weight.
Pipe supports are built to counter these forces, and quality piping solutions will lengthen the lifespan of your whole piping system.
First, supports should reduce corrosion. This usually means adding insulation that discourages metal-on-metal corrosion. Because galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals interact, supports can stop this destruction by insulating pipes.
Pipe supports can also strengthen systems by physically reinforcing them. In some instances, they can add a protective barrier between the pipe’s surface and surrounding harsh surfaces. In this way, supports can prevent ruptures and tears.
At the same time, an efficient support will reduce friction and the wear that results. When a pipe rubs against surrounding surfaces, it becomes vulnerable to cracks, tears, and corrosion. With every small opening that forms, corrosive materials are able to seep in and cause damage. Pipe supports also help pipes move more fluently so they can avoid ruptures or fitting failures.
Wondering how pipe shoes fit into this equation? Pipe shoes should have the same broad goal as other pipe supports. However, they accomplish these goals in a unique way.
Chapter 2
What Is a Pipe Shoe?
If you want to keep pipes from scraping against surrounding surfaces, the natural way to do this is to lift them off of the surface. This is where a pipe shoe comes in.
Pipe shoes lift piping off of I-beams or other surfaces. By elevating pipes, shoes insulate them from surrounding objects. What’s the advantage? Using a pipe shoe is a way to avoid the problems of metal-on-metal contact that can easily damage your pipes or existing supports.
First, they can stop pipes from rubbing against dissimilar metals. That means they’re able to prevent electrochemical transfer and galvanic corrosion.
Bare pipes that rest on surrounding objects are subject to grinding, friction, and wear.
For instance, your pipes may be made up of carbon steel. If the surrounding I-beams are made of a more noble metal, like stainless steel, then resting bare carbon pipes directly on beams is dangerous. In time, the electrons from your carbon pipes will pass into the more noble stainless-steel beam. This results in a carbon pipe that’s eaten away or weakened. In this case, pipe shoes lift carbon pipes off of the dissimilar metal of the beam and protect them.
Even if metals are compatible, shoes can prevent destruction. Pipes can move for any number of reasons. Vibrations can cause pipes to shift, heat changes can cause pipes to swell or contract, and sloshing liquids inside pipes can create movement. As pipes move, pipe shoes keep different materials from grinding against each other. In the same way, they minimize the movement and direct wear that comes with temperature changes.
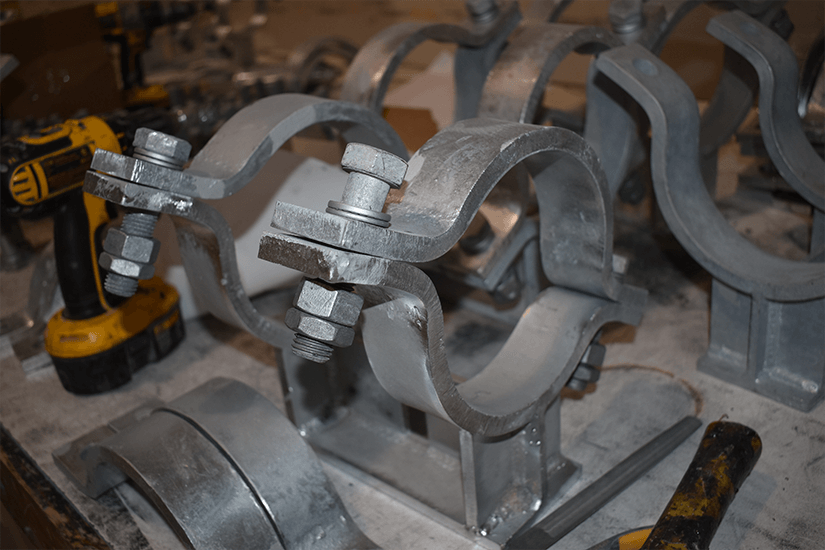
This is especially apparent in systems that face extreme cold, like liquid natural gas (LNG) plants. In these cases, even if the connected metals get along, they encourage damaging ice formation. Because metals are conductive, the metal of the beam will encourage heat transfer in pipes. Heat naturally wants to flow between metals. This means metals that touch encourage thermal contraction, ice formation, moving pipes, and surface damage. Well-insulated pipe shoes will help stabilize pipe temperatures and keep heat from exiting or entering pipes.
Regardless of temperature and external conditions, bare pipes that rest on surrounding objects are subject to grinding, friction, and wear. Temperatures and corrosive environments amplify damage. In turn, pipe shoes keep pipes from grinding, tearing, and leaking.
Finally, and most importantly, pipe shoes can allow for a safer working environment because they make it possible to install insulation and personal protection cages on pipe that is too dangerous for workers to be exposed to or touch. By elevating the pipe, the line can be fully encapsulated—creating a safer working environment and reducing the risk of injury.
Overall, by lifting pipes off of other surfaces, pipe shoes help pipes maintain their integrity. They prevent metal-on-metal contact and reduce friction damage. Essentially, they can insulate pipes, give them structural support, and promote natural movement.
Although the advantages of pipe shoes outweigh the disadvantages, there are still some things to look out for. When looking at the potential disadvantages of pipe shoes, it’s good to remember that materials matter. Unprotected metal shoes have the potential for corrosion if they’re not paired with the right insulation.
At the same time, there are natural concerns to consider when pipe shoes are welded directly to supporting beams. Anytime welding occurs, there is potential for stress cracking, especially in chloride-heavy environments like sea air. This means it’s usually well worth making sure that all welds are heat treated and welded by professionals.
Chapter 3
Types of Pipe Shoes
Broadly speaking, pipe shoes can be separated by material and makeup. Traditionally, pipe shoes have been made of metal and can come as large pre-insulated fixtures. More recently, composite pipe shoes have made their way onto the scene. Each different shoe has its own unique qualities, capabilities, advantages, and disadvantages. Here’s an overview of the different pipe shoe types:
Traditional metallic pipe shoes have been common in the industry for decades. In the past, manufacturers have designed metallic pipe shoes using structural shapes from cost-effective materials. For instance, manufacturers might use I-beams or channel beams to form a shoe. Right away, it’s easy to see the benefits of using these simple materials to form a pipe shoe. They’re made of materials that are easy to access and a wide range of suppliers can make them. They also tend to be fairly low cost and aren’t overly complex to install or produce.
However, there are some disadvantages to these traditional shoes. First, using any type of unprotected metal for a shoe can be dangerous. Pairing up dissimilar metals can lead to corrosion underneath the welded shoe. They also aren’t ideal for systems that undergo heavy temperature changes because metal-on-metal pairing can encourage ice formation and wear
Beyond these relatively simple traditional shoes, there are more advanced T-style metallic pipe shoe designs. Often referred to as T-slides, some of these metallic shoe options feature cradles and U-bolts, or two clamps to hold the pipe in place.
Beyond having a slightly more intentional design than that of traditional shoes, these metallic shoes have advantages of versatility. Many T-style pipe shoes can be paired with wear pads or other liners. This eliminates metal-on-metal contact, allows for better control of a shoe’s movement, and can provide greater protection to the piping system.
Other metallic shoes can be built from other channel material or plate to any custom dimensions. The major advantage of this is that you get exactly what you want. But as is the case with anything custom, you will have to pay for that flexibility, and the price can become prohibitive when compared to that of other options.
Metallic shoes can be welded directly to the pipe in a pipe fabrication shop or in the field. When installing, it’s always a good idea to use professionals and welders who uphold industry standards such as MSS SP-58. Additionally, using U-bolts or clamps to install piping is no more complicated than using a wrench.
Composite pipe shoes offer a corrosion-resistant alternative to metallic shoes. Still, composite materials are often misunderstood. Because they don’t have the same rigid makeup of metal, it’s common for some to assume that composites are weak. However, they can actually be extremely durable. Here’s a look at some popular composite pipe shoes that are available today:
The ProTek composite pipe shoe is a UV-resistant, non-metallic pipe support that is built to withstand heavy pressure and especially hot and cold temperatures. It has 150,000 pounds of compressive strength, a temperature range of -320 to +400 degrees Fahrenheit, and is resistant to chemical attack. Because of its makeup, it has become a popular option for corrosion-heavy systems such as onshore and offshore refineries and plants.
They also offer an advantage in the way they fit against pipes. They fit against piping snugly, with their inner diameter crafted to fit the pipe’s outer diameter precisely. This essentially keeps corrosive elements from sneaking in between the pipe and the support. With a precise fit, the shoe seals off vapors and stops corrosive materials from settling on pipes.
ProTek shoes don’t require specialized installation. They’re lightweight and don’t require welding. The installation process includes simply fixing the shoe to the pipe using steel bands and silicone.
CryoTek shoes are a sturdy option that can handle a bit more of an axial load than ProTek shoes can.
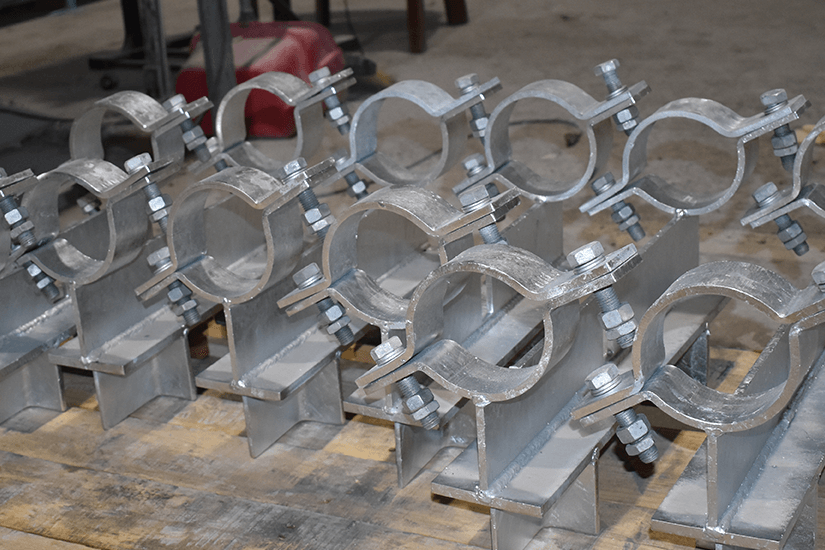
CryoTek composite pipe shoes have quickly become a popular item in cryogenic piping systems that involve gas liquefaction, LNG terminals, carriers, and ethylene plants.
They have the same corrosion protection and operating temperature advantages as ProTek shoes (-320 to +400 degrees Fahrenheit). However, CryoTek shoes are a sturdy option that can handle a bit more of an axial load than ProTek shoes can. In fact, they have a maximum compressive strength of 27,500 pounds per square inch. They include well-defined insulation that protects piping. Their design also makes them a sturdy option for a stop or anchor. Despite their robust design, these supports are also easy to transport.
Additionally, they offer an advantage in their ability to eliminate heat sync. Their insulation features banding slots inside the shoe, which stay inside the insulation and prevent any heat from entering or escaping.
Because both CryoTek and ProTek shoes are much lighter than their metallic counterparts, they offer an installation advantage over traditional metal shoes. Installation also doesn’t require welding or specialized labor.
CryoTek shoes are installed using a powerful epoxy. They can be bonded using a static epoxy mixer, which takes the guesswork out of mixing two-part epoxy. From there, the bonded shoe is reinforced with steel metal bands.
Pre-insulated pipe shoes generally consist of hefty stainless steel bodies and an encapsulating insulation foam between the pipe and the stainless steel body to keep the line insulated.
The biggest advantage of pre-insulated shoes is that they come installed and ready to go.
However, with their size and makeup comes some disadvantages. On jobs that require transportation, they can be difficult to maneuver, and setting them in place requires specialized lifting equipment. They also generally come with a relatively hefty price tag.
Pre-insulated pipe shoes need to be installed by professionals on-site or pre-fabricated and moved. They generally require heavy, specialized equipment, precise procedures, and professional welders.
Chapter 4
Getting the Most Out of Your Pipe Shoe
As you choose a pipe shoe that best fits your system, you’ll want to determine which factors are most important to you. We’ve laid out common determining factors to consider while you’re on the hunt for the perfect pipe shoe, as well as ways of getting more out of the shoe you ultimately choose.
When considering your budget, it’s a good idea to keep total costs in mind. Of course, that starts with the price of each unit. However, it also means deciding how many units you’ll need, the cost of installation, and the long-term costs that may result down the line. Here’s a general look at the costs of pipe shoes:
Metal T-style shoes can be some of the most cost-effective shoes out there. However, some low-end T-styles can run the risk of corrosion on their own. Countering that disadvantage leaves room for creativity. It’s a good idea to factor in corrosion protection options when weighing this shoe’s overall costs.
The price of metal T-style shoes with clamps can vary, especially depending on which liners you decide to pair them with. However, as a whole, they tend to have a midrange cost, plus the ability to make upgrades by pairing them with things like wear pads or slide plates.
At the composite end, ProTek shoes tend to be the more affordable option. In fact, they often come in under or close to the price of their metallic counterparts. CryoTek prices can vary, but they tend to be a good deal more expensive than their ProTek counterparts.
This is the simplest application for pipe supports and its objective is simply to support the load of the pipe and allow for the free movement of the piping system.
In both resting and guided supports, pipe shoes can be used in conjunction with slide plates fastened to the underside of the shoe’s base. These plates are generally sodium-etched PTFE that’s bonded to 10-gauge carbon or stainless steel. The PTFE is usually paired with a polished stainless steel plate that’s attached to the beam to allow for one of the lowest coefficients of friction possible. At the same time, it promotes more natural movement and less wear.
These supports are used when you want to restrict most, if not all, pipe support movement. These can be fixed to a point—preventing movement in the axial, lateral, and vertical directions.
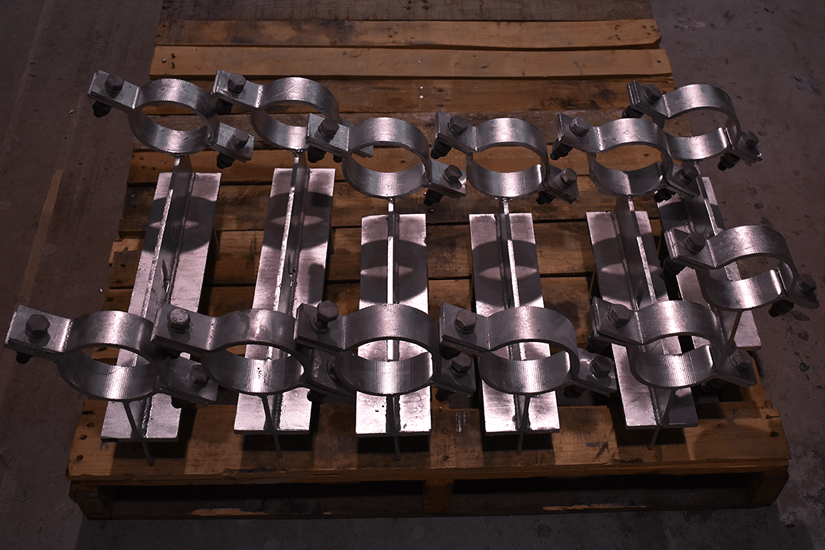
Beyond costs, there are several other factors to weigh when making your final pipe shoe selection. First, always think about how well the shoe’s composition, design, and features will fit into your specific system.
For instance, if you’re operating an offshore rig that’s exposed to salt-heavy conditions, you may want to place more emphasis on corrosion-resistant materials. At the same time, if your system is fairly calm and protected from the elements, it may be smarter to focus on shoes with a lower upfront cost.
With those factors in mind, here are some helpful questions to ask in order to get more out of your pipe shoes:
As soon as you’ve picked out the right shoe, you can start to benefit from its unique advantages. For instance, metallic shoes with clamps can be enhanced by adding specialized liners or wear pads. These additions stop metal-on-metal contact and help both pipes and supports last longer.
Chapter 5
Technology Trends and the Future of Pipe Shoes
As manufacturers work to make shoes more efficient in extreme conditions, pipe shoes are being paired with more complex types of insulation.
One interesting material that may hold completely new possibilities for the advancement of pipe shoes is the use of aerogel composite blanket insulation. Although it is a bit more expensive than traditional insulation options, it’s a viable option in many applications with some pretty spectacular properties.
Aerogel is a flexible, high-performance blanket insulation designed to mitigate corrosion under insulation (CUI)—a process by which elements seep into crevices and cause corrosion inside insulation—in both high- and low-temperature applications. It was engineered to deliver superior thermal performance while offering protection against CUI. Because CUI is a major concern with respect to pipe shoes due to their function of elevating insulated lines, we’re always watching out for the latest technological advancements that will better prevent corrosion. Aerogel is picking up steam in its use around the globe due to its many beneficial properties.
Because CUI is a major concern with respect to pipe shoes due to their function of elevating insulated lines, we’re always watching out for the latest technological advancements that will better prevent corrosion.
In the future, manufacturers will also work to solve existing problems. One interesting advancement in CUI prevention has been the arrival of directly applicable thermoplastics. This new technology is best known as a product that is sold by the company Oxifree. Essentially, it is applied to fixtures using a heated pistol. The substance coats the area that’s susceptible to corrosion, which forms a thermoplastic coating that keeps contaminants out and weatherproofs pieces. This is an excellent option when you’re dealing with simple T-style supports that may be welded to your support when you’re battling corrosion.
Final Thoughts on Pipe Shoes
Overall, pipe shoes can fight off the natural dangers that pipes face, and they can lengthen the lifespan of your process piping system. Ignoring the need for the appropriate supports can lead to corrosion, system breakdowns, and on-site disasters.
However, the more you understand about the role of pipe shoes, the different types of pipe shoes, and the advantages of each, the easier it is to incorporate them into your system the right way. In turn, with this knowledge in hand, you should be ready to pick out the right solution to avoid destruction and help you get the most out of your entire system.

